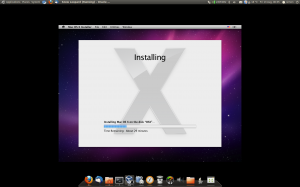
I have always wanted to install OSX as a virtual machine. I tried about a year ago with a vmware image which was so slow. So i thought i would give it a another try after hearing that VirtualBox >=3.2 supports OSX. I was actually quite surprised at the speed it runs at it is reasonably snappy. The only think it really lacks is 3d support so that you good use the seamless mode. And change the resolution to some better than 1024×768.
Indicator Applet Thunderbird Support
Thunderbird does not have the Ubuntu indicator support at the moment. Only evolution is has full indicator support at the moment but i prefer to use Thunderbird. So here is how to get a basic Thunderbird starter in your indicator applet:
create a file named ‘thunderbird’ in /usr/share/indicators/messages/applications
nano /usr/share/indicators/messages/applications/thunderbird
and add the following:
/usr/share/applications/thunderbird.desktop
Thats it save the file and you should be able to start Thunderbird from the indicator applet
Change Document Root Plesk
1. In the directory
/var/www/vhosts/example.com/conf create a file called vhost.conf
2. Edit the file with a text editor and add the following line:
Documentroot /my/new/DocumentRoot
3. Then execute the following command
/usr/local/psa/admin/sbin/websrvmng -–reconfigure-vhost -–vhost-name=example.com
4. Okay thats it reload the apache webserver
/etc/init.d/apache2 reload
Ubuntu Firefox won’t play flash movies
To get firefox to play flash movies in ubuntu do the following. First make sure you have the adobe flash player installed:
aptitude install flashplugin-installer
This should enable flash in firefox after restarting firefox. One additional problem i had is due to compiz the flash movie player would show up in firefox. But pressing the play button had no effect. Do the following:
Edit the file: /usr/lib/nspluginwrapper/i386/linux/npviewer and add the following line:
export GDK_NATIVE_WINDOWS=1
Thats it have fun watching flash movies on ubuntu
Debian/Ubuntu Package management Using dpkg
Dpkg is the Debian package manager dpkg is a tool to install, build, remove and manage Debian packages.
Now we will see all the available commands for dpkg with some examples
1)Install a package
Syntax
dpkg -i <.deb file name>
Example
dpkg -i courier-pop-ssl_0.61.2-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
2)Install all packages recursively from a directory
Syntax
dpkg -R
Example
dpkg -R /usr/local/src
3)Unpack the package, but don’t configure it.
Syntax
dpkg --unpack package_file
If you use -R option is specified, package_file must refer to a directory instead.
Example
dpkg --unpack courier-pop-ssl_0.61.2-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
4)Reconfigure an unpacked package
Syntax
dpkg --configure package
If -a is given instead of package, all unpacked but unconfigured packages are configured.
Example
dpkg --configure courier-pop-ssl_0.61.2-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
5)Remove an installed package except configuration files
Syntax
dpkg -r
Example
dpkg -r courier-pop-ssl_0.61.2-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
6)Remove an installed package including configuration files
Syntax
dpkg -P
If you use -a is given instead of a package name, then all packages unpacked, but marked to be removed or purged in file /var/lib/dpkg/status, are removed or purged, respectively.
Example
dpkg -P courier-pop-ssl
7)Replace available packages info
Syntax
dpkg --update-avail
With this option old information is replaced with the information in the Packages-file.
8)Merge with info from file
Syntax
dpkg --merge-avail
With this option old information is combined with information from Packages file.
The Packages file distributed with Debian is simply named Packages.dpkg keeps its record of available packages in /var/lib/dpkg/available.
9)Update dpkg and dselect’s idea of which packages are available with information from the package pack-age_file.
Syntax
dpkg -A package_file
10)Forget about uninstalled unavailable packages.
Syntax
dpkg --forget-old-unavail
11)Erase the existing information about what packages are available.
Syntax
dpkg --clear-avail
12)Searches for packages that have been installed only partially on your system.
Syntax
dpkg -C
13)Compare Package versions version numbers
Syntax
dpkg --compare-versions ver1 op ver2
14)Display a brief help message.
Syntax
dpkg --help
15)Display dpkg licence.
Syntax
dpkg --licence (or) dpkg --license
16)Display dpkg version information.
Syntax
dpkg --version
17)Build a deb package.
Syntax
dpkg -b directory [filename]
18)List contents of a deb package.
Syntax
dpkg -c filename
19)Show information about a package.
Syntax
dpkg -I filename [control-file]
20)List packages matching given pattern.
Syntax
dpkg -l package-name-pattern
Example
dpkg -l postfix
21)List all installed packages, along with package version and short description
Syntax
dpkg -l
22)Report status of specified package.
Syntax
dpkg -s package-name
Example
dpkg -s openssh-server
23)List files installed to your system from package.
Syntax
dpkg -L package-Name
Example
dpkg -L postfix
24)Search for a filename from installed packages.
Syntax
dpkg -S filename-search-pattern
Example
dpkg -S /usr/bin/cut
25)Display details about package
Syntax
dpkg -p package-name
Example
dpkg -p openssh-server
If you want more information about dpkg check “man dpkg”
Plesk drweb antivirus update cron mails
A cron is run every 30 minutes to check on virus database updates via /etc/cron.d/drweb-update, which sends an email every 30 minutes to the plesk server admin. Most of our customers don’t like the behavior.
To resolve, direct the output to /dev/null or to a log file instead if you need to keep a watch on the updates.
1. Edit /etc/cron.d/drweb-update redirecting the output to /dev/null
vi /etc/cron.d/drweb-update
2. Add the following line
*/30 * * * * drweb /opt/drweb/update.pl >/dev/null 2>&1
This would direct all out put from the drweb update script to /dev/null (trash)
Confixx + Postfix+ IMAP + Maildir
This howto describes howto get rid of the horrible mboxes for mail which confixx uses by default. Converting all your mailboxes to the maildir format also allows you to use imap. Please make backups of your confixx installation before you begin with this howto you have been warned:
1. Edit your confixx main.conf
vi /root/confixx/confixx_main.conf
When your finished this is what it should look like:
$maildrop = ‘HOMEDIR/Maildir/’;
$mailBoxName = ‘Maildir’;
$pop_homeDir = ‘/var/mail’; //specify folder where you want maildirs to be stored. the folder must exist
$mail_realHome = ’1?;
2. Edit your postfix main.cf
vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
And add the following line:
home_mailbox = Maildir/
3. Edit your procmailrc
vi /etc/procmailrc
And add the following line:
DEFAULT=”$HOME/Maildir/”
4. Run the confixx counterscript
/root/confixx/confixx_counterscript.pl –fa -dbg
5. Convert existing Mboxes to Maildir. Confixx provides a script for doing this. Run the script and make sure to answer all the questions. Or except the defaults which should be ok.
/root/confixx/admin/contrib/convert_mb2md.pl
6. If you are using qpopper uninstall it and install courier pop and imap if you need imap. This is for debian and ubuntu:
aptitude purge openbsd-inetd qpopper
aptitude install courier-pop
aptitude install courier-imap
Thats it check you log files send a test mail and enjoy.
X11 Forwarding with SSH
This is fairly simple stuff but it took me 15 minutes to solve because i was missing a package 🙁 So i thought i would write a quick article here we go X11 forwarding with ssh. This should work on any Linux distribution unless ssh has been built without the support for X forwarding. Which as far as i know is uncommon.
1. Install xauth with your package manager for ubuntu/debian do
aptitude install xauth
2. Edit the sshd_config on the server you want to start the X program from
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
3. Add the following to your sshd_config file on the server
X11Forwarding yes
4. Restart the ssh server
/etc/init.d/ssh restart
5. Edit the ssh_config on the client (this could also be in your home directory under .ssh/config)
vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config
6. Add the following to your ssh_config file on the client
ForwardX11 yes
7. Connect to the server with ssh
ssh user@host
8. You can also use ssh -X user@host Which switches on X Forwarding for the single connection. We don’t need this option because we set it permanently in the ssh_config on the client.
How do I change the address Qmail sends the MAILER DAEMON messages to
By default Plesk administrator’s email address is listed in:
/var/qmail/alias/.qmail-mailer-daemon
/var/qmail/alias/.qmail-postmaster
/var/qmail/alias/.qmail-root
You can edit these files and set the email address you need.